In this topic, we discuss anatomy. You will learn about:
- the anterior and posterior views of the body
- joint movements (extensions and flexions)
- types of muscle contractions.
Terminology and vocabulary reference guide
As an allied health professional, you need to be familiar with terms associated with basic exercise principles and use the terms correctly (and confidently) with clients, your colleagues, and other allied health professionals. You will be introduced to many terms and definitions. Add any unfamiliar terms to your own vocabulary reference guide.
Activities
There are several practical activities in the topic and an end of topic automated quiz. These are not part of your assessment but will provide practical experience that will help you in your work and help you prepare for your formal assessment.
The study of anatomy and physiology provides the foundation to understand the parts of the body and their functions. This knowledge is critical for a personal trainer.
Anatomy is the study of the body's structures or parts. It essentially asks the question ‘What is that? And where is it in the body?
Physiology studies the functions of the body parts and asks the question ‘What does it do?’
Whilst they individually focus on different aspects of the study of the body, they are often studied together as structure (anatomy) and function (physiology) of the body is closely related. In this topic, we focus on anatomy as it relates to exercise techniques and working safely and effectively.
The anterior and posterior views of the body
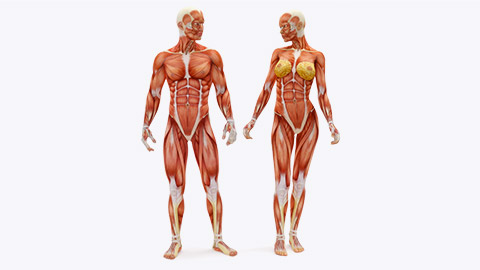
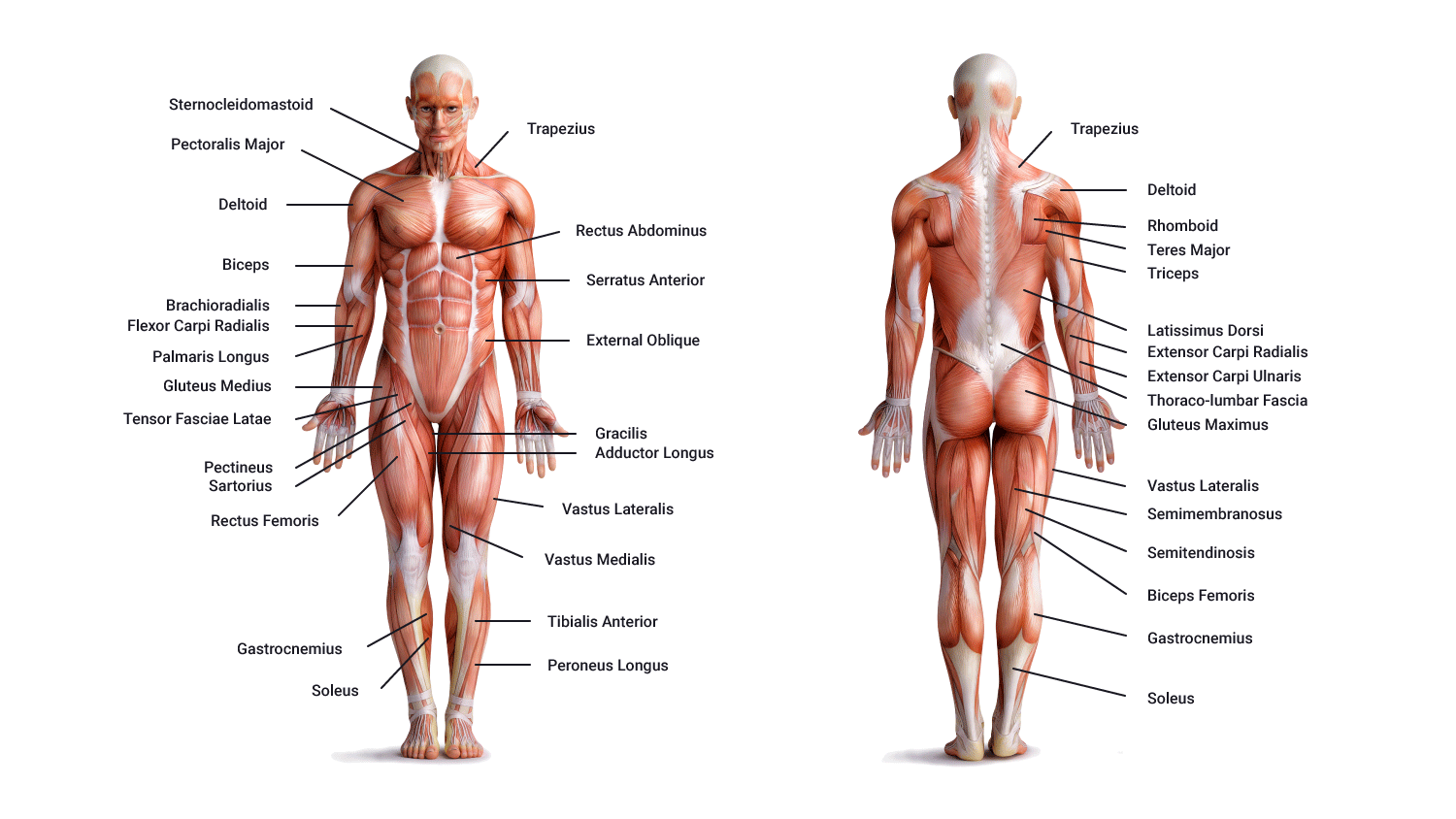
As a personal trainer, you also need to know what is meant by the anterior and posterior views of the body. You may find instructions or guidelines that refer to these terms. The anterior body refers to the front of the body. The posterior view shows the back of the body. The following images show both views and key muscles you will be working with as a personal trainer.
Joint movements
You will also come across the terms flexion and extension and you need to be clear on what these mean in relation to exercises. Many of the exercises you teach clients will involve joint movements which will be either flexions or extensions. So, what is the difference?
- Flexion: Flexion decreases the angle between the bones (bending of the joint)
- Extension: Extension increases the angle and straightens the joint.
For example, for the upper limb, all anterior-going motions are flexion and all posterior-going motions are extension. Now, look at the following two images and study the labels.
You may have noticed two other terms: adduction and abduction. Medical and fitness professionals use a common language to describe movements of the human body.
- Adduction: Adduction refers to a movement towards the midline of the body. Think of an imaginary line running down the middle of a body or any limb.
- Abduction: Abduction is the opposite to adduction and is when a body part moves away from the midline.
The following video will explain more about flexion and extension joint movements.

Simply put, muscle contractions involve movements that shorten a muscle while a person is exercising. There are four main types of muscle contractions you need to understand. They are described briefly below.
| Type of contraction | Description |
|---|---|
| Isometric | Tension is developed within the muscle but no movement or change in joint angle occurs. That is, the force developed by the muscle is equal to that of the resistance. |
| Isotonic | Tension is developed in the muscle while it either shortens or lengthens. Classified as either concentric or eccentric. |
| Concentric | Muscle develops tension as it shortens. Muscle develops enough force to overcome resistance. |
| Eccentric | Muscle lengths under tension and occurs when the muscle gradually lessens its tension to control the descent of weight. |
The following video will expand on this information. The video which provides a good summary and general overview of how the muscular system works, including the three main muscle types, including the skeletal muscles which are of interest to us in this Module.
Watch until 3:26 which focuses on the skeletal muscles shown in the illustrations above, muscle contractions and movements. These are all important concepts for trainers.
Now for a fun video that claims to teach you the main muscles in a three-minute song!
Vocabulary reference guide
Make a list of anatomical terms and labels for the muscles of the body and any common terms you are aware of. While it is true you will probably use the common terms a lot, it is important (and enhances your professional reputation) when you use the correct terminology with your colleagues, clients, and other professionals. Don't forget to add any unfamiliar terms (including common names) to your own vocabulary reference guide.
You may also wish to use the internet to find three resources that you could use to help explain how muscle contractions work with your clients. Think about what would help your client understand the different contractions and when they might occur. You might come across YouTube clips, websites, images, illustrations, or documents. Keep a list for future reference and for sharing with others.
Anatomy and physiology are important banks of knowledge you need to be an effective and competent personal trainer.
In this topic, you learnt about:
- the anterior and posterior views of the body
- joint movements (extensions and flexions)
- types of muscle contractions.

