In this topic, we focus on the implementation of a various analytical tools and how they are used to analyse and evaluate the organisations position. You will learn:
- The SWOT analysis and how it is used to evaluate your organisations strengths and minimise any potential threats
- The PEST analysis and how this tool is used to analysis factors that are out of your control and how your organisation can adapt to any external factors that may be presented
- The Five Forces analysis which determines who competition may be for your business and how it may impact on your profitability.
Terminology and vocabulary reference guide
As an allied health professional, you need to be familiar with terms associated with basic exercise principles and use the terms correctly (and confidently) with clients, your colleagues, and other allied health professionals. You will be introduced to many terms and definitions. Add any unfamiliar terms to your own vocabulary reference guide.
Activities
There are several practical activities in the topic and an end of topic automated quiz. These are not part of your assessment but will provide practical experience that will help you in your work and help you prepare for your formal assessment.
When both setting up and reviewing your business after a period of running time, it is crucial to complete an analysis of the current situation to see if your initial plan at set up is working and is effective. A SWOT analysis is the ideal tool in order for you to establish what is your and your business strengths weakness opportunities and threats. By conducting a SWOT analysis, it enables you to establish what you do well and what you may be lacking in order to maximise success. This is a useful risk-analysis tool to help avoid pitfalls and provide you with the greatest opportunity for business progression.
What is SWOT?
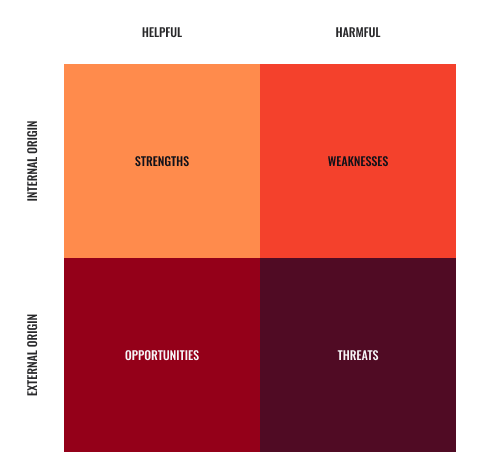
SWOT is based on the following four components:
- Strengths: this refers to internal capabilities and resources such as knowledgeable staff, skill level of the team, things you and your company do well, and qualities that separate you from your competitors. Strengths can also include tangible items such as equipment, technologies, and intellectual property. Strengths are seen as positives within the SWOT matrix.
- Weaknesses: refer to skills or knowledge your company or team lack, areas where your competitors may excel at in comparison to you, and any resource limitations you currently have, essentially, internal weaknesses. These are seen as negatives within the SWOT matrix.
- Opportunities: refer to positive factors or trends in the external environment that your business and or team may be able to exploit to its advantage, such as unserved areas of the market, emerging needs of your niche.
- Threats: refer to negative external factors or trends that may present challenges to the performance or success of your business such as emerging competitors, changes to regulations within your environment, negative press you or your industry may have received or changing attitudes towards your customers.
A SWOT analysis is not a one-time event, this should be done on a regular basis in order to assess both external factors which may negatively impact your business along with the internal factors to establish if they remain supportive of the business.
Picture your organisation running successfully, clients are pouring in the door on a regular basis, a gym opens up next door. This would be considered a threat to your organisation and therefore needs to be monitored and perhaps a strategy developed as to how this can be responded to, i.e. effective planning.
How to fitness SWOT
A SWOT analysis should be included as part of your market research. When you have identified your customers and competitors as well as review your business strategy and position, a SWOT analysis becomes essential.
Below are some examples of questions you may ask yourself in regard to each component of the SWOT analysis.
Strengths
These reflect your business does very well. Some questions you could be asking to recognise the business’s strengths may include:
- What are your strengths in relation to your competitors?
- What advantages do you have over others in the industry?
- What do you do well?
- What relevant resources do you have access to?
- What do people see as your strengths?
The following are other aspects to consider:
- Your specialist marketing expertise
- A new, innovative product or service
- Location of your business
- Quality processes and procedures
- Any other aspect of your business that adds value to your product or service.
Weakness
These reflect where the internal and external weaknesses of your business lie. Some questions you could be asking to identify weaknesses in the business may include:
- What could you improve on? Be honest
- What should you avoid?
- What are the critical issues to address?
- How can the business overcome weaknesses?
- Are there weaknesses that you do not know about or can identify?
Other important areas to consider:
- The location of your business
- A lack of marketing or business expertis
- Poor quality of training equipment or services
- Damaged reputation.
Opportunities
Keep a lookout for any trends, changes within the industry or in the marketplace that you could capitalise on. Some questions you could be asking to seize, and opportunity may include:
- Where are there good opportunities facing you?
- Where are the best opportunities?
- How can the opportunities be captured?
- Is technology being utilised in the best way?
Other important areas to consider are:
- Developing markets
- Mergers, joint ventures, or franchises
- Moving into new market segment
- International markets or ideas from abroad
- A market vacated by an ineffective competitor.
Threats
These are external factors that can have a negative impact on the business’ ability to achieve its goals and outcomes. Some questions you could be asking to help determine potential threats to the business may include:
- What obstacles or constraints do you face?
- What is your competition doing?
- Is changing technology an issue?
- Are legislation and regulatory requirements changing?
- Do you have bad debt or cash flow problems?
- Are there new competitors in your area?
Other important areas to consider are:
- Price comparisons with competitors
- New innovative products or services introduced by competitors
- Existing products becoming unfashionable or unpopular
- Rising costs.
The following table is an example of the potential results of a SWOT analysis within a fitness organisation.
| Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|
|
|
| Opportunities | Threats |
|
|
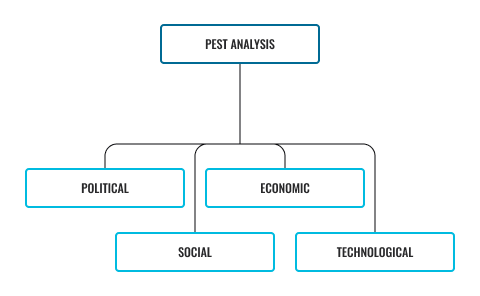
A PEST analysis is a strategic business tool used by organisations to help them understand their environment. It thoroughly analyses factors that are outside of the control of the business however will likely impact its success. Click on each of the following factors to learn more.
- Monopolies legislation
- Environmental protection laws
- Taxation policies
- Employment laws
- Government policy legislation.
- Inflation
- Employment
- Disposable income
- Business cycles
- Energy availability and cost.
- Demographics
- Distribution of income
- Social mobility
- Lifestyle changes
- Consumerism
- Levels of education
- New discoveries and innovations
- Speed of technology and transfer
- Rates of obsolescence
- Internet
- Information technology
By completing a PEST analysis, you will be able to evaluate your strategies and to adapt to any external factors that may be presented. It also provides a support to assist with planning, marketing, and development to cater to any influences that your business could be exposed to in the future.
Porters Five Forces is another analysis undertaken by various businesses to determine who competition may be for their business and how it may impact on their profitability.
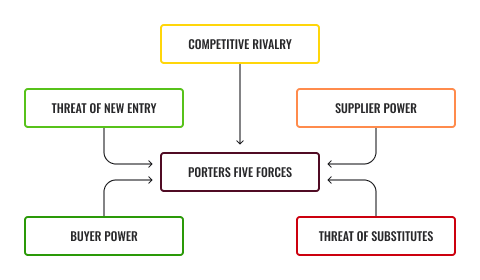
Competitive rivalry within industry
The first of the five forces refer to the number of competitors and their ability to undercut another business. Are they able to provide equivalent products for a better deal or lower prices? When competitive rivalry is low then a business can charge higher prices to achieve higher sales and profits, however, when there is competition, prices need to remain competitive which can impact on the profits you receive.
The following are some examples on how competitive rivalry can influence the profitability of a business.
- Number of competitors
- Quality differences
- Switching costs
- Customer loyalty
- Cost of leaving market.
Threat of new entrants
The second refers to new entrants entering the industry, the less time and money it may cost a competitor to enter the market will deem them to be competition. This may be exhibited through the fitness industry as new personal trainers begin to enter within your community which could potentially create a concern for you and your current clients.
The following are some examples on how threat of new entrants can influence the profitability of a business.
- Time and cost of entry
- Specialist knowledge
- Economies of scale
- Cost advantages
- Technology protection
- Barriers to entry.
Power of suppliers
This is the next factor that focuses on how easily suppliers can drive up the cost of resources. If your supplier decides to charge more for their products, then this will impact on your costs and profitability as you pay more but may be forced to sell at the same price to stop the risk of losing customers.
The following are some examples on how power of supplies can influence the profitability of a business.
- Number of suppliers
- Size of supplies
- Uniqueness of service
- Your ability to substitute
- Cost of changing.
Bargaining power of buyers
The fourth force that explains the importance of customers and how they can dictate the profitability of your business. It reflects on how important your customers are, how they are valued and how a long-term client base can continue to drive up your profits. Without happy client’s profitability may seize to exist.
The following are some examples on how buyer power can influence the profitability of a business.
- Number of customers
- Size of each order
- Differences between competitors
- Price sensitivity
- Ability to substitute
- Cost of changing.
Threat of substitution
The last force within Porter’s Five Forces is known as threat of substitutes. If your business can provide a service which there are close to no substitutes, then the business will have the ability to increase prices however if customers have an option to shop around and see equivalent products elsewhere this will be considered a threat.
The following are some examples on how threat of substitution can influence the profitability of a business.
- Substitute performance
- Cost of change.
Some questions that may need to be asked to successfully complete an analysis using Porter’s Five Forces include:
- What industry are you in?
- Who are your competitors both directly and indirectly?
- What are your strategies to support you in managing any potential threats?
Reflecting on this information, take a moment to identify who your competitors may be specific to the fitness industry and how you can use the Five Force analysis to help minimise any risks or challenges to your business.
In this topic, we focused on the implementation of various analytical tools and how they are used to analyse and evaluate the organisations position. You learnt:
- The SWOT analysis and how it is used to evaluate your organisations strengths and minimise any potential threats
- The PEST analysis and how this tool is used to analysis factors that are out of your control and how your organisation can adapt to any external factors that may be presented
- The Five Forces analysis which determines who competition may be for your business and how it may impact on your profitability.

