In the world of design, collaboration is essential for innovation and successful project outcomes. This topic focuses on the power of working together and effectively communicating with others. You will learn to identify key contributors within the design process, understand their roles, and explore how to use their expertise to enhance your design.
By unlocking the potential of collaboration and integrating feedback effectively, you can refine your work and create compelling designs that meet project objectives and exceed client expectations.
Subtopics include:
- Unlocking the Power of Collaboration
- Identifying Key Contributors in the Design Process
- Using Feedback to Enhance Your Design.
Three key collaborative stages in the graphic design workflow, where diverse perspectives are integrated to enhance creativity and project outcomes.
Tip
Gearing up for assessment: Project collaboration
As you work through this topic, the information you’ll focus on – including collaborating with others to enhance the design process, inviting critical analysis, and acting on feedback – are key to completing some of your project planning assessment tasks in Part B of Assessment 2 (Project and Portfolio).
In the assessment, you'll plan your collaborative interactions to inform and enhance the graphic design process and collaborate with a contributor using communication and collaborative techniques. Use the guidance provided here to develop strategies that ensure productive collaboration and improve your design outcomes.
Learning Tasks That Will Help You Develop and Practise Graphic Design Skills
Practice
Use your skills and build your knowledge of collaboration.
Dive into this topic’s three learning tasks confidently – they're your stepping stones towards getting to grips with how to collaborate and liaise with others. Completing these tasks will reinforce your knowledge around collaboration tools and constructive criticism.
Look out for this PRACTICE box throughout this topic to identify learning tasks with instructions to let you know exactly what to do. The following information outlines what learning tasks to expect in Topic 3 and how much time you should allocate to each one.
| # | Learning task name | Duration |
|---|---|---|
| 9 | Check your knowledge: Collaboration tools in graphic design | 5 minutes |
| 10 | Practice – Looking back at collaborative feedback and its impact | 30 minutes |
| 11 | Check your knowledge: Characteristics of constructive criticism | 5 minutes |
Reach out for feedback and support if you have any questions about what to do!
This subtopic will guide you through key aspects of unlocking the power of collaboration. It includes the following sections:
- Benefits of collaborative design
- The collaborative edge in action
- Putting collaboration into practice
- Identifying your network.
Benefits of Collaborative Design
In graphic design, collaboration involves integrating diverse perspectives to produce visually compelling designs. It ensures that various aspects of a project benefit from different expertise and viewpoints.
Select + to read about three key benefits of collaborating and liaising with others in graphic design:
Multiple individuals bring different skills and perspectives, leading to richer and more dynamic visual designs. These individuals are not just designers; the design itself results from creative ideas involving different individuals and skill sets, including users, developers, marketing specialists, and clients.
Collaboration integrates varied design approaches, helping to create designs that appeal to the target audience. People working in isolation rarely get things perfect on the first try, and good design takes critique and feedback to get it right. The more you hone an idea/concept leveraging other people’s perspectives, the better your solution becomes.
Group efforts in brainstorming and feedback can quickly address graphic design challenges and refine concepts. Collaboration drives graphic design in the right direction.
For example, suppose a team realises the initial project requirements were incorrect. In that case, they can contact stakeholders to discuss the issue, introduce necessary changes and restart the design process.
Explore
Go further together: Unleash your potential through the power of collaborative design.
To further explore how collaboration can enhance your career as a graphic designer, consider the adage, “If you want to go fast, go alone. If you want to go far, go with a pack.” This perspective underlines the value of collaborating to achieve greater success and overcome the challenges of the graphic design industry.
Watch this video (5:20 mins), where Adrian Boysel, a seasoned graphic designer, shares insights and tips on thriving in a collaborative environment. By working together with a diverse group of professionals, you can create compelling work for your clients and grow as a graphic designer.
The Collaborative Edge in Action
In graphic design, collaboration is more than just a buzzword; it’s a fundamental component that drives creativity, integrates diverse perspectives, and facilitates efficient problem-solving. By leveraging the collective expertise of a team, designers can achieve more innovative and comprehensive solutions.
Effective collaboration is essential for achieving successful outcomes in graphic design, as it underscores the importance of clear communication and teamwork in preventing project setbacks and failures.
This collaborative edge is exemplified in the following two case studies of Dropbox’s logo redesign and Spotify’s Wrapped campaign, where collaboration among diverse teams played a crucial role in their resounding success.
Case Study
Enhanced creativity: How Dropbox's collaborative approach redefined Its identity
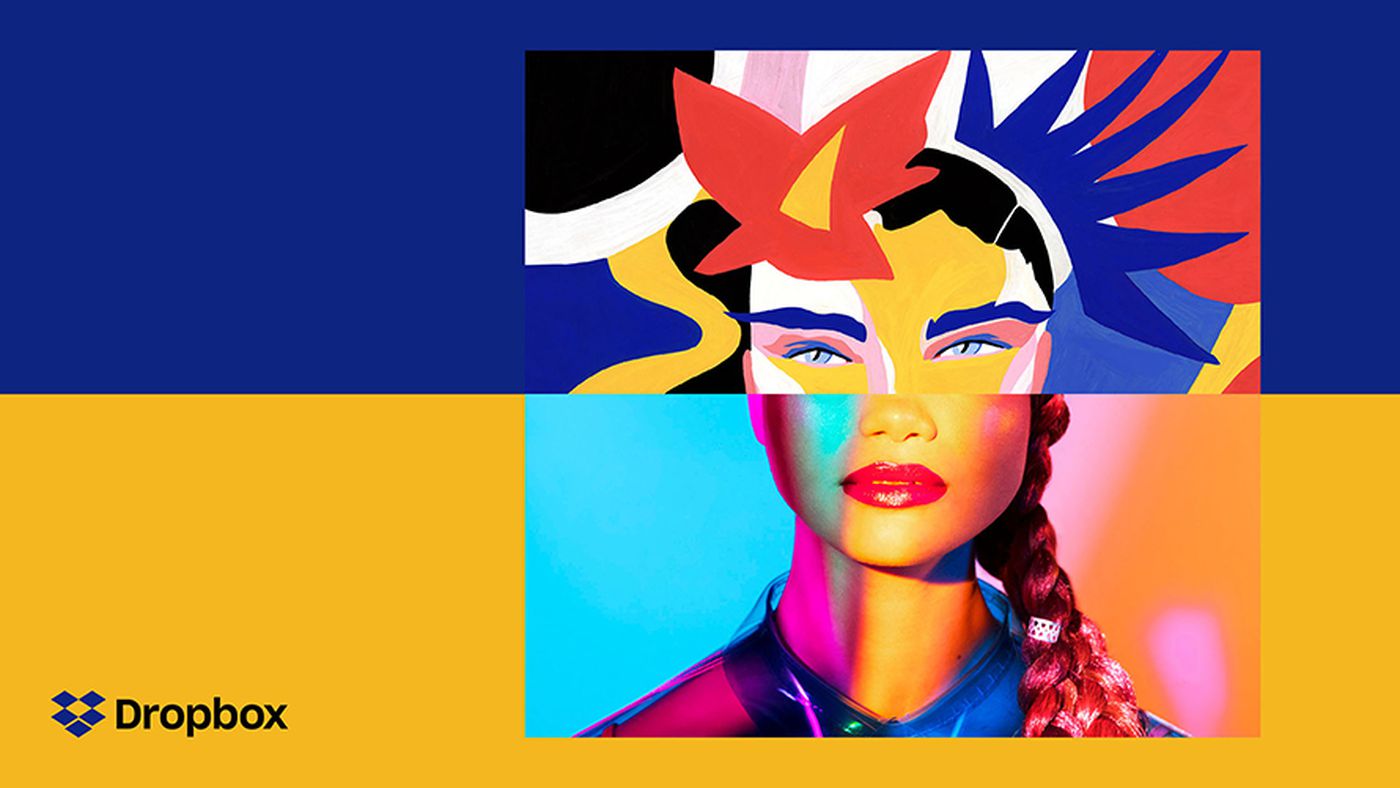

Dropbox’s logo redesign in 2017 is a prime example of effective collaboration. The company worked with multiple designers, strategists, and engineers to overhaul its visual identity. The team aimed to reflect Dropbox's evolution from a file storage service to a collaborative platform.
By involving a diverse group of individuals, they were able to create a logo that not only updated the brand's image but also communicated its broader capabilities. The redesign process involved extensive feedback loops and iterative refinements, which allowed the team to address various challenges and align the logo with the company’s vision.
Reflecting on Dropbox's use of contrasting colours and imagery in their logo redesign, how do you think the principles of collaboration—such as integrating diverse perspectives and unexpected ideas—contributed to the design's success?
Additionally, consider how Dropbox itself as a collaborative platform influenced the redesign process. How can you apply collaborative principles and tools to enhance your own graphic design projects?
Case Study
Wrapped: A symphony of collaboration that brings personalised music experiences to life.

Spotify’s Wrapped campaign is a collaborative masterpiece that has become an annual highlight for the streaming service. The project involves designers, data analysts, marketers, and engineers working together to create a personalised summary of each user's listening habits over the past year.
This project highlights the importance of cross-functional collaboration, where the integration of creative design, data visualisation, and user engagement strategies resulted in a campaign that not only enhanced the user experience but also boosted Spotify’s brand loyalty and social media presence. The success of Spotify’s Wrapped campaign underscores how collaborative efforts can lead to highly engaging and successful marketing initiatives.
Consider this quote from the article about the Wrapped campaign: “It’s the result of a special company-wide collaboration between teams across Spotify. As Global Head of Marketing Experience, Louisa Ferguson builds those connections across every moment of the campaign strategy, end-user journey, and global roll-out.”
How can building connections across different teams and stages of a graphic design project contribute to a more effective and cohesive outcome? Think about how such collaboration could enhance your design projects and the role of teamwork in achieving successful results.
Putting Collaboration Into Practice

Effective collaboration in graphic design involves not only understanding the value of working together but also applying practical techniques and tools to streamline the process.
This section will:
- explore key techniques for successful collaboration
- introduce tools to facilitate collaborative work
- provide you with tips for integrating these tools into your design workflow.
Techniques for Successful Collaboration
To check your current understanding of key collaboration techniques, match each of the three collaboration techniques in the quiz below with its corresponding purpose.
Take a moment to review how to implement each collaboration technique by reading the table below. Knowing these methods will help you practise these techniques with others in your graphic design projects to enhance your creativity and solve problems.
| Collaboration technique | How to achieve |
|---|---|
| Regular Check-ins and Updates |
|
| Brainstorming Sessions |
|
| Clear Communication |
|
Practising and applying effective these collaboration techniques is crucial for fostering a productive and creative team environment.
BARILLA DESIGN PROJECT

Design is a team sport: Coordinating for success.
In the early stages of Barilla's packaging redesign, Kelley establishes a collaborative workflow by scheduling regular check-ins with Barilla’s marketing team and product developers. These meetings ensure alignment, enable prompt feedback, and address challenges early on.
Kelley also organises brainstorming sessions that create an open space for creativity to thrive.
By fostering clear communication and defining roles, the team successfully integrates modern and traditional design elements, laying a solid foundation for the project’s success.
To enhance these techniques and streamline the collaborative your graphic design process, using the right tools and platforms can also make a significant difference. In the next section, explore various tools and platforms designed to support and enhance collaborative efforts, helping you implement the techniques you've reviewed more effectively.
Tools to Facilitate Collaboration
In graphic design projects, where creativity and precision are paramount, having the right tools can significantly enhance teamwork, streamline workflows, and improve project outcomes.
Various categories of collaboration tools exist which are essential for graphic designers, including:
- Project management tools
- Communication platforms
- Design collaboration tools
- File sharing and storage solutions
By leveraging these tools and platforms, you can enhance your collaborative efforts, improve project efficiency, and achieve better outcomes.
Important
Unleashing the potential of diverse collaboration tools
As a graphic design student, it's important to understand that the tools and platforms featured in this topic are just a starting point and are examples for you to see how tools can facilitate collaboration.
Each tool offers unique features that can enhance your collaborative efforts and streamline your design process.
Dive into different options, experiment with their capabilities, and find the ones that best fit your project needs and team dynamics. Your ability to effectively use these tools will not only improve your design outcomes but also prepare you for real-world collaborative environments.
Select each of the four categories in the following interaction to reveal examples and features of some collaborative tools and platforms. Click the expand icon in the bottom right to enter fullscreen mode for a better view. When you're ready to return, click the icon again to exit fullscreen.
Practice
Task 9: Check your knowledge – Collaboration tools in graphic design
This quiz is designed to help you identify the most effective tools and techniques for collaboration in graphic design projects. By understanding the strengths and best uses of different platforms, you can enhance your ability to brainstorm, ideate, and gather feedback, ultimately leading to more successful and creative design outcomes.
What steps should you take to complete this task?
Set aside 5 minutes to complete this knowledge check.
- This quiz has four questions. Read each question carefully. Make sure you understand what is being asked before attempting an answer.
- Provide the most accurate and complete answers you can. If a question stumps you, make an educated guess based on your knowledge.
- Don't let difficult questions discourage you. Stay confident and do your best. Remember, it's a learning opportunity, and not a formal assessment!
- Once you've reviewed your answer and are satisfied, click the ‘Check button’ to see if you chose the correct answer. You can also retry questions and show solutions.
What should you do after completing this task?
Now that you've identified the best tools for various collaborative tasks, it's time to explore how to integrate these tools into your design workflow. In the next section, learn practical strategies to make the most of these platforms, ensuring smooth and productive collaboration throughout your projects.
Integrating Collaboration Tools Into Your Design Workflow
To effectively integrate collaboration tools into your design workflow, it’s essential to understand their features and benefits.
Using the right collaboration tools can streamline your projects, enhance teamwork, and ultimately lead to better design outcomes. Below are three key considerations to help you maximise these tools.
1. Identify your needs
Determine what your design workflow requires. Do you need project management features, real-time collaboration, or file-sharing capabilities? Understanding your needs will help you choose the most appropriate tools.
2. Explore options
You may have noticed that there are numerous collaboration tools available, each offering unique features. It’s important to explore and evaluate which ones align best with your workflow.
Explore
Ten best design collaboration tools for every situation
This Filestage guide to design collaboration software article provides a succinct overview of various design collaboration tools available in the market (as of August 2024).
It outlines their features, benefits, and use cases, helping you make an informed decision about which tool might be the best fit for your needs.
Assess your unique 2-D or 3-D graphic design workflow needs to select the most effective collaboration tools. What criteria will you use to evaluate these options?
3. Integrate and test
Once you’ve assessed and chosen your tools, integrate them into your workflow and test them with your team. Gather feedback and adjust as necessary to ensure the tools are enhancing, not hindering, your design process.
Explore
Ten best design collaboration tools for every graphic design situation
Watch Megan Weeks, a work-from-home graphic designer, review ten essential tools she uses in her daily business operations to help her communicate, share work, and manage her projects.
The video (19:59 mins) highlights the functionalities of these tools (you can scrub to the tool you’re interested in if you don’t want to watch the entire video) and offers insights into how you can integrate them into your collaborative workflow.
Identifying Your Network
In any graphic design project, the strength of collaboration is not just in the tools you use but in the people who come together to bring a vision to life.
Effective collaboration hinges on involving the right individuals who can contribute their unique skills and perspectives to enhance the design process. As you prepare to explore the next subtopic, Identifying Key Contributors to the Design Process, consider how your network's design diversity and expertise can elevate your work's quality and creativity.
Think about the collaborative experiences you've had so far:
- Who were the key players, and what roles did they fulfil?
- How did their contributions impact the outcome of the project?
- What challenges did you encounter during the collaboration, and how did you overcome them?
Identifying these individuals and understanding their influence can help you appreciate the importance of strategic collaboration. It’s not just about having a team with tools; it’s about having the right team, one that aligns with the project's objectives.

This subtopic will guide you through key aspects of identifying key contributors in the design process. It includes the following sections:
- Identifying your key contributors
- Engaging your contributors for success.
Identifying Your Key Design Contributors
Understanding the value of key contributors is fundamental to ensuring the design process is thorough and effective. The contributors you select can significantly influence a project’s direction, efficiency, and outcome. This section will explore why identifying and involving the right people is crucial for a successful design project.
Why Is Valuing Key Contributors Essential?
Valuing key contributors involves recognising their unique skills and understanding how their involvement can lead to a more successful and efficient design process.
Select + to read about three main reasons why key contributors are essential to design projects and processes.
Diverse knowledge: Key contributors bring specialised knowledge and skills that enhance the overall quality of the design. For example, a UX designer could provide insights into user behaviour and needs, while a graphic designer could focus on visual aesthetics.
Informed decisions: Engaging the right people ensures that design decisions are well-informed and based on expert input, leading to more effective solutions.
Holistic approach: Involving various roles in the design process ensures that a team considers all aspects of the project, helping identify potential issues early and integrating diverse perspectives into the final design.
Balanced design: By incorporating feedback from different experts, the design becomes more balanced and addresses multiple facets of the project, such as usability, functionality, and visual appeal.
Clear responsibilities: Clearly defined roles and responsibilities improve team coordination and minimise overlaps. Each contributor focuses on their area of expertise, leading to a more efficient workflow.
Streamlined process: Effective collaboration among team members reduces miscommunication and ensures that tasks are completed on time, contributing to the project’s overall success.
Who Are Key Contributors?
In any design project, several key contributors play critical roles. Each brings unique expertise and insights that are essential to the project's success.
When searching for contributors, look for individuals who possess specific qualities. Drag each of the four qualities to their matching description to check your grasp of what these qualities are.
What Are Their Roles and Responsibilities?
In a typical design project, different roles work together to achieve the project goals.
Critical roles are performed by clients, designers, industry experts, project managers, and developers.
Flip each card below to gain an overview of the key contributor roles you should identify.
How Do You Find the Right Contributors for Your Design Project?
While your design project in this module will be your own individual effort, collaborating with others can significantly enhance your process and results.
Here are some techniques to help you effectively involve peers and industry professionals in your design project:
- Collaborate with peers: Engage with your classmates to share ideas and progress. Collaborative discussions can lead to new insights, constructive critiques, and suggestions you might not have considered.
- Consult your tutor: Your tutor is an excellent resource for expert advice. They can guide you through complex design decisions and connect you with industry professionals who can provide specialised input.
- Involve family and friends: Share your project with family and friends to gather their opinions and suggestions. Their diverse perspectives can help you identify strengths and weaknesses in your design.
- Explore online communities: Join platforms like Behance, Dribbble, or design forums to connect with a broader community of designers. Engaging with these platforms allows you to receive critical feedback of your work from experienced professionals and fellow designers.
- Review case studies and portfolios: Review the work of established designers through their portfolios and case studies. Understanding their design choices and problem-solving methods can inspire you to adopt similar approaches.
- Act on feedback: Collect and use the constructive criticism you receive to refine and improve your design. Reflect on the critiques and suggestions and consider how they can be incorporated to enhance your project’s overall quality.
Practice
Task 10: Looking back at collaborative feedback and its impact
Engage in a reflective exercise to evaluate how collaboration and feedback have influenced your design work. This is crucial for understanding how diverse perspectives can enhance your projects, much like how Kelley used collaborative feedback to improve her team’s strategies when working on the Barilla project.
What tools or resources do you need for this task?
- Documenting tool (e.g. Microsoft Word or similar) for creating a document that details your reflection.
What steps should you take to complete this task?
Set aside up to 30 minutes to complete this task.
- Identify key collaborators: Reflect on any projects or activities where you worked with others, whether they were design-related or not. Identify the key contributors (e.g., peers, family, friends). What roles did they play in your design process?
- Review feedback received: Summarise the feedback you received from each collaborator, such as thumbnails, design ideas, and the design brief. How did their input influence your design?
- Detail actions taken: Describe the specific actions you took based on the feedback. What changes did you make to your design ideas or other project elements?
- Reflect on the Impact: Reflect on how incorporating feedback and collaborating with others influenced your design process and the final product. What benefits did you gain from their input? How did their contributions shape your approach to the project?
- Save your work: Document your reflections and save the document. Be ready to discuss how the insights you gained from this task could apply to the Barilla project, including how collaboration and feedback might address any identified issues or opportunities.
What should you do after completing this task?
- Share your reflection to forum:
- Select your forum thread in the Coursework Forum.
- Select Reply to your first Forum post.
- Enter the words ‘Task 10: Collaboration’ in your new post.
- Select the Post your response button, then select Edit in your reply when it shows up.
- Upload your documented objectives in the Attachment field.
- Select Save changes to share your coursework to your forum thread.
- Post constructive feedback on other students’ coursework and receive feedback on your coursework from your tutor and other students.
Having identified and reflected on your previous key collaborators and the feedback they provided, you're now ready to explore the next crucial step in your collaboration journey - Engaging your contributors effectively - where you will learn how to actively involve your collaborators, harness their strengths, and foster a collaborative environment that drives project success. Make sure to apply the insights from your reflection to build stronger, more effective collaborative relationships as you move forward.
Engaging Your Contributors for Success
Engaging with contributors in a productive and organised manner can significantly enhance the outcome of your work. This section will explore effective communication strategies, techniques for productive collaboration, and real-world examples of stakeholder engagement to help you maximise the success of your project.
What Are Some Effective Communication Strategies?
Effective communication is the foundation of successful contributor engagement. Here are four strategies to ensure clear and productive interactions with your contributors:
| Strategy | Interactions |
|---|---|
| 1. Establish clear objectives | Begin by defining the goals and expectations for your project. Ensure all contributors understand the project's objectives and their individual roles in achieving them. |
| 2. Set up regular check-ins | Schedule regular meetings or updates to discuss progress, address challenges, and align on tasks. Consistent communication helps keep everyone on the same page and facilitates timely problem-solving. |
| 3. Use clear and concise language | When sharing information, be direct and specific. Avoid jargon or ambiguous terms that might lead to misunderstandings. |
| 4. Provide constructive criticism | Offer feedback in a manner that is helpful and respectful. Highlight specific areas for improvement, offering practical suggestions for change while recognising what is working well. |
Communicating with clients
Effective communication with a client – a key contributor - is essential for the success of any design project. Clear and concise language helps in avoiding misunderstandings and ensures that everyone involved is on the same page.
BARILLA DESIGN PROJECT

Key contributors: Aligning client expectations.
In the Barilla packaging redesign project, Kelley prioritises clear and effective communication with the client to ensure alignment.
By using concise language and adapting her approach by using more questions, she ensures client expectations are clearly understood, and feedback is efficiently managed. Kelley focuses on preventing misunderstandings, keeping both her, Lee, and the client on the same page.
Detailed documentation and visual explanations support the feedback process, reinforcing clarity and maintaining coherence throughout the project, leading to a better chance of a successful design outcome.
Watch Benjy Kaiser (6:32 mins) , a digital marketing manager with a background in graphic design, provide practical insights into handling client communications. He offers strategies to ensure alignment with client expectations and a streamlined revision process.
To help reinforce the key strategies discussed in the video, try this short quiz to give you a chance to reflect on how you can apply these communication techniques in your own projects.
What About Techniques for Productive Collaboration?
To enhance the productivity of your engagement efforts, consider the following four techniques:
- Define roles and responsibilities: Clearly outline the roles and responsibilities of each contributor to help avoid overlaps and ensure that everyone knows their specific tasks and contributions.
- Use collaboration tools: Leverage digital tools and platforms designed for team collaboration. Tools such as Slack, Trello, or Microsoft Teams can help manage tasks, share files, and facilitate communication.
Explore
Leveraging tools for team collaboration
If you haven’t already, take some time to look at the previous Unlocking the Power of Collaboration subtopic to discover collaboration tools exist which are considered essential for graphic designers, including:
- Project management tools
- Communication platforms
- Design collaboration tools
- File sharing and storage solutions
Follow these breadcrumbs to learn more: 19.3. Collaborate and liaise with others > 19.3.1 Unlocking the power of collaboration > Putting collaboration into practice > Tools to facilitate collaboration.
- Foster an inclusive environment: Encourage input from all contributors and value their contributions. An inclusive approach helps generate diverse ideas and solutions.
- Resolve conflicts constructively: Address conflicts or disagreements promptly and constructively. Focus on finding solutions rather than assigning blame.
These productive collaboration techniques feature in the following case study of the comprehensive redesign of the New York Times website. This project illustrates effective collaboration among diverse teams to achieve a unified and adaptable design that could evolve seamlessly.
Case Study
The New York Times redesign project
Background
In 2014, The New York Times comprehensive redesigned its website and digital platforms. The project aimed to enhance user experience, update the visual identity, and create a more responsive and engaging platform for its readers.
Collaborative process
- Cross-functional teams: The project involved a large team of graphic designers, UX/UI designers, developers, and editorial staff. These diverse groups collaborated closely, bringing together different perspectives and expertise.
- Open communication: Regular meetings and open communication channels were established to keep all team members informed and involved. This transparency helped maintain alignment on project goals and allowed for quick adjustments as needed.
- Inclusion of diverse perspectives: The project emphasised the inclusion of diverse perspectives, both within the team and from the audience. By considering the needs of various demographic contributors, the design team created a more inclusive and accessible website.
- Design sprints and workshops: The team conducted design sprints and workshops to brainstorm and prototype new ideas. This agile approach allowed for rapid testing and iteration of design concepts, ensuring that each iteration was informed by collective input and feedback.
- User-centred design: User research was a critical component of the redesign process. The team engaged with various stakeholders, including readers, to gather insights into their preferences and pain points. This feedback directly influenced design decisions, from typography choices to navigation structures.
Outcomes
- Consistent visual identity: The new design maintained the integrity of The New York Times brand while modernising its visual language.
- Enhanced user experience: The redesign led to a more intuitive and engaging user interface, improving overall user satisfaction.
- Positive reception: The redesigned platform received positive feedback from users and critics alike, showcasing the success of a collaborative and inclusive design process.
This case study illustrates how The New York Times leveraged collaborative techniques and inclusivity to successfully revamp its digital presence, highlighting best practices in graphic design project management.
Consider the following questions as you reflect on engaging with key contributors in your own design project:
- How can fostering an inclusive environment in your graphic design projects enhance creativity and ensuring that the final product resonates with a broader audience?
- How can incorporating diverse perspectives into your design process lead to more innovative and user-friendly design solutions?
- In what ways can effective communication and regular feedback loops improve alignment within your team and help achieve your project goals?
As you approach the end of this subtopic, it's essential to recognise how collaboration extends beyond initial interactions - identifying and understanding the key contributors and their roles is just one part of a successful design process. The next step involves asking and taking in feedback, which is not just a component of collaboration but a vital element in advancing your design.
In this topic’s final subtopic – Using Feedback to Enhance Your Design – you’ll explore embracing constructive criticism and using feedback to refine your design as you transition into development. This feedback process will help you fine-tune your work and strengthen your ability to adapt and evolve as a designer, ensuring that your final product meets the design brief’s objectives and resonates with your audience.

This subtopic will guide you through key aspects of using feedback to enhance your design. It includes the following sections:
- Embracing constructive criticism
- Using feedback to improve your design.
Embracing Constructive Criticism
Constructive criticism is a cornerstone of the design process, essential for refining your work and achieving excellence. In this section, explore what constructive criticism is and its value in enhancing your design work,
What Is Constructive Criticism?
Constructive criticism in graphic design refers to feedback that provides specific, actionable, and insightful comments aimed at improving the design.
It focuses on enhancing various aspects of a design, such as visual appeal, functionality, and usability, while maintaining a supportive tone. The goal is to offer guidance that helps you as the designer refine your work to better meet project objectives and audience needs.
Characteristics of constructive criticism in graphic design
The table below outlines the essential aspects of constructive criticism specifically tailored to graphic design, providing examples of how feedback should be delivered and used.
| Characteristic | Description | Graphic Design Example |
|---|---|---|
| Specific and actionable | Feedback should provide clear, detailed suggestions on specific elements of the design, such as colour, typography, and layout. | Instead of saying "The design isn’t good" say "The contrast between the background and text needs adjustment. Consider using a darker shade for better readability." |
| Supportive | Feedback should be delivered in a manner that encourages and motivates improvement, rather than discouraging the designer. | Rather than criticising the design harshly, acknowledge what’s done well and suggest, "The layout is well-organised, but the font size for headers should be increased for better readability." |
| Balanced | Constructive criticism should highlight both strengths and areas for improvement, providing a comprehensive view of the design. | Instead of focusing solely on flaws, provide balanced feedback: "The colour palette is vibrant and engaging, but the text could be more readable with a higher contrast colour." |
Practice
Task 11: Check your knowledge – Characteristics of constructive criticism
This quiz is designed to test your knowledge of different characteristics of constructive criticism. By evaluating various feedback examples, you’ll sharpen your ability to recognise and interpret constructive critiques, ensuring that feedback effectively contributes to design improvements.
What steps should you take to complete this task?
Set aside 5 minutes to complete this knowledge check.
- This quiz has six questions. Read each question carefully. Make sure you understand what is being asked before attempting an answer.
- Provide the most accurate and complete answers you can. If a question stumps you, make an educated guess based on your knowledge.
- Don't let difficult questions discourage you. Stay confident and do your best. Remember, it's a learning opportunity, and not a formal assessment!
- Once you've reviewed your answer and are satisfied, click the ‘Check button’ to see if you chose the correct answer. You can also retry questions and show solutions.
What should you do after completing this task?
With this insight into feedback types, the next section will explore the value of constructive criticism. Discover how effective feedback drives improvement and contributes to achieving successful design outcomes.
What Is the Value of Constructive Criticism?
Constructive criticism is not just about pointing out flaws; it plays a pivotal role in enhancing your design work. Understanding its value helps you refine your designs and fosters a culture of continuous improvement.
Identifying strengths and areas for improvement
Constructive criticism offers a balanced perspective by highlighting both strengths and areas needing improvement. This comprehensive feedback helps you recognise what is working well and what can be enhanced.
By focusing on specific aspects of your design, feedback enables you to make informed adjustments that lead to a more polished and effective final product.
Fostering innovation and effectiveness
When embraced positively, constructive criticism can drive innovation. Feedback often introduces new ideas or alternative approaches that you might not have considered. By integrating these suggestions, you can explore creative solutions and refine your designs to better meet user needs and project goals.
This iterative process of receiving and applying feedback ensures that your designs are not only functional but also innovative and impactful.
Enhancing overall design quality
Incorporating feedback into your design process contributes to higher quality outcomes. Constructive criticism helps you address potential issues early on, resulting in more effective designs that meet the project’s objectives and resonate with your target audience.
This ongoing refinement process leads to more successful design projects and helps you grow as a designer.
Tip
Reflect on your own experiences to refine your creative journey
As you delve deeper into understanding the value of inviting and acting on feedback in your design process, it’s essential to take a moment to reflect on your experiences and approaches. Consider the following questions to gain insights into how you can enhance your ability to invite, receive, and integrate feedback effectively:
- How do you typically react to constructive criticism, and what emotions does it evoke in you?
- What specific examples of constructive criticism have significantly improved your design work in the past?
- How can you ensure that you’re effectively integrating feedback into your design process without losing your unique design vision?
Reflecting on constructive criticism enables you to better understand your reactions, experiences, and the integration of feedback into your design work. Using this reflective practice not only fosters professional growth but also contributes to the overall quality and effectiveness of your design projects.
Using feedback to improve your design
Effectively using feedback is key to improving your design work. This section explores practical methods for inviting, receiving, and integrating feedback to enhance your design process and outcome.
Use the feedback loop to refine and align your designs with project objectives.
1. Inviting Feedback on Your Design
Define clear objectives
Before seeking feedback, clarify the specific aspects of your design you aim to improve. This focus ensures that the feedback you receive is actionable and directly relevant to your goals.
Identify relevant reviewers
Choose individuals with relevant expertise or experience—peers, mentors, clients, or target users—to provide insightful feedback.
Remember to consider the diverse perspectives that different reviewers can offer and how they might highlight unique aspects of your design.
Provide context
Share the background, goals, and current status of your design with reviewers to ensure their feedback is informed and meaningful.
Tip
Set the Stage: Context is key to meaningful feedback.
Draft a summary of your project to provide context for your reviewers when inviting their feedback, including the design's background, goals, and current status.
2. Receiving Feedback on Your Design
Be open-minded
Being open-minded is essential when receiving feedback. Approach feedback as an opportunity for growth, not as personal criticism. Embrace different perspectives and be willing to challenge your assumptions.
Explore
Embrace feedback: A guide to turning critiques into growth opportunities.
Watch this insightful video (4.44 mins) from Creative Director Explains, where valuable strategies for embracing and applying feedback in graphic design are discussed.
After watching the video, reflect on the following questions:
- How can you shift your mindset to view feedback as an opportunity for growth rather than a personal critique?
- How can asking clarifying questions enhance your understanding of the feedback and its relevance to your work?
- How does taking time to reflect on feedback contribute to making more informed revisions to your work?
- How do you plan to use feedback to make necessary revisions, and how does this demonstrate your commitment to personal and professional growth?
By strategically incorporating feedback into your revisions, you set the stage for exploring effective methods to using feedback in enhancing your design process.
Clarify and ask questions
If any feedback is unclear, seek clarification to understand it accurately and apply it effectively.
The table below outlines key questions to ask when clarifying feedback, the purpose of each question, and examples of how they could be applied in a graphic design context. Use clarifying questions to effectively interpret feedback, ensure alignment with project objectives, and make well-informed revisions to your designs.
| Question | Purpose | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Can you provide specific examples or details to illustrate your feedback? | To understand the exact issues or suggestions being made. | "Can you show me exactly where the colour choices you mentioned need improvement?" |
| What specific aspects of my design do you think need improvement? | To direct feedback to particular elements for focused revisions. | "Which parts of the layout do you feel are not meeting the design objectives?" |
| Are there any particular design principles or criteria that I should consider while making these revisions? | To align revisions with design standards and principles. | "Should I follow a specific style guide while making these changes?" |
| How do you think these changes will impact the overall effectiveness of the design? | To assess the potential outcomes and relevance of the feedback. | "Will adjusting the typography affect the readability and user experience?" |
| Is there any additional context or information that I should consider when addressing your feedback? | To gather extra details that might influence the revisions. | "Is there any user feedback that I should integrate into the design?" |
| Can you clarify the priority of this feedback compared to other aspects of the design? | To prioritise feedback and focus on the most critical issues first. | "Should I address the colour scheme adjustments before refining the layout?" |
Take notes
Document all feedback to ensure you can refer to it during the design revision process. Use collaborative tools such as shared documents, project management platforms, and feedback tracking software to organise and manage the feedback received from various stakeholders.
This not only helps in maintaining a clear record but also facilitates easy access for team members, ensuring that all relevant input is considered and integrated into the design efficiently.
3. Integrating Feedback Into Your Design
BARILLA DESIGN PROJECT

Feedback matters: Enhancing design through input.
When presenting two packaging design concepts for Barilla—one sleek and contemporary, the other nostalgic—Kelley and Lee received client feedback that the minimalist option might stray too far from the brand’s identity.
To address this, Kelley categorised the feedback into usability, functionality, and aesthetics, allowing for clearer analysis and prioritisation. Kelley then created an action plan to integrate the client’s input, focusing on revisions that maintain Barilla’s brand heritage.
Lee iterated on the design, incorporating classic elements like the signature blue and historic logo into the minimalist concept. By blending modern design with traditional elements, the team ensured the packaging appeals to both new and loyal customers.
Integrating feedback into your design projects involves systematically refining your work and achieving superior results. This section provides you with an organised approach to incorporating feedback into your design process, ensuring that insights are applied to enhance your final outcome.
Organise and prioritise feedback
Categorise the feedback
Group feedback into categories such as:
- usability
- functionality
- aesthetics.
This approach helps in addressing specific aspects of the design more efficiently.
Develop an action plan
Create a plan outlining how you will address each piece of feedback. Prioritise these change tasks based on their impact on the design and alignment with project goals. This ensures that the most critical feedback is acted upon first.
Implement feedback in design
Make iterative revisions
Apply feedback through iterative changes. Revise your design progressively, testing each version to evaluate the effectiveness of the modifications. This iterative approach helps in making continuous improvements.

Integrate feedback through iterative changes.
Important
Balance feedback with design integrity
Feedback must be contextualised and addressed according to its source.
For example, suppose a client requests a colour change to better match the target audience. In that case, this feedback should be incorporated if it aligns with the client’s brief.
However, if feedback contradicts the brief, have a discussion with the client to resolve the discrepancy.
Maintain the overall design vision and coherence while integrating feedback. Avoid changes disrupting the design’s integrity or deviating from the original objectives!
Watch this video (3:54 mins) to hear Dharam discuss various types of feedback, their sources, and practical strategies for incorporating feedback while maintaining your design’s integrity.
To test your understanding of the points made in the video, complete the following quiz to help reinforce the key feedback integration strategies discussed and how you can apply these techniques in your projects.
Test and validate changes
Conduct usability testing
Test the updated design with real users or stakeholders to confirm that the feedback has improved usability and met their expectations. Gather additional feedback if necessary to make further adjustments.
Review with stakeholders
Present the revised design to stakeholders for their input and approval. This ensures that the design aligns with their expectations and project requirements.
Document and reflect
Keep comprehensive records
Keep detailed records of the feedback received, the changes made, and the rationale behind each modification. This record is valuable for tracking progress and learning from the process.
Reflect on the process
Evaluate how effectively feedback was integrated into your design. Reflect on the outcomes and identify areas for improvement in future projects.
As you move forward to future topics – i.e. Developing and Presenting Ideas for 2-D and 3-D Work and Realise 2-D and 3-D Designs – remember that the insights gained from using feedback are crucial throughout subsequent phases.
Feedback isn't just a preliminary step; it remains integral as you refine and present your ideas. Effective use of feedback enhances your designs, ensuring they align with project goals and client expectations. In this phase, you will delve into translating your concepts into detailed designs, clearly articulating your ideas, and presenting them to stakeholders.
The iterative nature of incorporating feedback will continue to guide you, helping to ensure that your final output is compelling and true to your refined design vision.
